New engineering techniques to deal with unmet oral health and fitness requirements
6 min readA baby bottle for children born with cleft palate. Chewing gum to crack up plaque and reduce tooth decay—or even COVID-19. A mouth guard that can detect infectious particles in saliva.
With assistance from the Centre for Innovation & Precision Dentistry (CiPD), these and other innovative strategies to solving oral-wellbeing-associated challenges are transferring from thought to reality.
The Center, released in January, has been awarded a important instruction grant from the National Institutes of Health, acquired awards for new technologies, and posted papers on the new conclusions. Plus it has established a community of partners to force each individual other ahead in researching and acquiring remedies to urgent worries in oral wellness care.
“Today, 3.5 billion individuals continue to have oral conditions that are preventable, these types of as tooth decay and periodontal ailment,” states Hyun (Michel) Koo, CiPD’s co-director and a professor in Penn’s University of Dental Drugs. “We will need to come up with extra precise, much more efficient strategies to target the people today who will need them the most and make guaranteed they are accessible and inexpensive.”
As a dentist and scientist with instruction in foodstuff engineering, Koo has viewed transformative improvements in health care technology arise and nevertheless not make a substantial impression on oral and craniofacial overall health in the United States or globally.
Previous calendar year, to accelerate development towards encouraging with these and other oral wellbeing situations, Koo and colleagues, which include Kathleen Stebe of Penn’s College of Engineering and Used Science, joined to start the CiPD. The exertion unites the two schools—and the respective abilities and resource inside of them—to aid ideas that can rework oral-craniofacial treatment and usher in new scientific treatments and preventive procedures to safeguard health.
“This partnership involving Penn Engineering and Penn Dental Medicine will progress new paradigms to assault oral health and fitness problems and prepare the up coming era of researchers steeped in engineering strategies in this place,” claims Stebe.
Tomorrow’s innovators
A major action ahead for the initiative came this summer season, when the scientists were awarded a T90/R90 grant from the National Institute for Dental and Craniofacial Exploration. The grant, titled “Advanced Instruction at the Interface of Engineering and Oral-Craniofacial Sciences,” will be co-led by Koo and Stebe and delivers approximately $2.5 million in excess of five many years to coach postdoctoral-level fellows at the intersection of the disciplines, supporting them utilize chopping-edge ways in engineering and computational sciences to examine disease mechanisms and create exact nevertheless lower-price diagnostics, therapies, and equipment.
“We’re hoping the grant will boost cross-pollination and build a culture involving these two fields to support dentists acquire progressive techniques with engineers,” says Koo. “Dentists can understand from engineering concepts and applications, and engineers can recognize a lot more about the demands of the dental and craniofacial fields. We’re offering a system for them to do the job collectively to tackle unmet medical requires and produce occupations in that interface.”
The instruction application, which plans to welcome its initial members this drop, aims to specially emphasis on the oral microbiome, host immunity, and tissue regeneration, every single of which ties into various elements of oral health, from tooth decay and periodontal disease to the wants of head and neck most cancers people. To advance these areas, rising strategies, from sophisticated materials, robotics, and artificial intelligence to chloroplast engineering and nanotechonology, will be leveraged.
With a determination to diversifying the workforce in this space, the application is partnering with universities typically underrepresented in postdoctoral education as well as minority-serving institutions to make a pipeline. They are also connecting with range packages in just the American Dental Affiliation and American Association of Dental Analysis.
As part of the two-year education, just about every postdoc will receive mentorship from clinicians, fundamental scientists, as well as engineers. These mentorships will be centered on research results and readying participants to post grants and contend for positions in academia or business.
“This is a career-defining prospect for excellent postdoctoral scientists to outline new engineering, computational, and utilized science methods in the oral overall health routine,” suggests Stebe. “We hope extremely enthusiastic scholars are captivated by the program’s tailor made-match instruction and support.”
Part of the application will entail partnerships with marketplace, so the postdoctoral trainees can extra deeply have an understanding of products growth and regulatory hurdles. “The trainees will be checking out the R&D facilities of Colgate-Palmolive and Johnson & Johnson so they can see the underpinnings of how research consequence receives to marketplace,” claims Koo. And the CiPD staff hopes to recruit far more firms to engage with the trainees.
Plaudits and help
To motivate established researchers and clinicians to commit time toward tasks that leverage engineering in aid of conference oral wellbeing demands, the CiPD is awarding seed funds that deal with gaps in oral wellness requires and do so in a charge-successful way.
In a partnership with Jason Moore of the Perelman University of Medicine’s Institute for Biomedical Informatics (IBI), the Middle is checking out artificial intelligence apps to discover new techniques to evaluate significant facts and forecast ailments, structure far more effective therapies, and evaluate the usefulness of current kinds.
A collaborative do the job concerning Shuying (Sheri) Yang of Penn Dental Medication and Michael Mitchell of Penn Engineering, supported by CiPD seed funds, led to a new Section of Protection grant. Their challenge investigates inflammatory mediators and ionizable lipid nanoparticles to produce drugs against bone defects, which has implications for persons with craniofacial diseases.
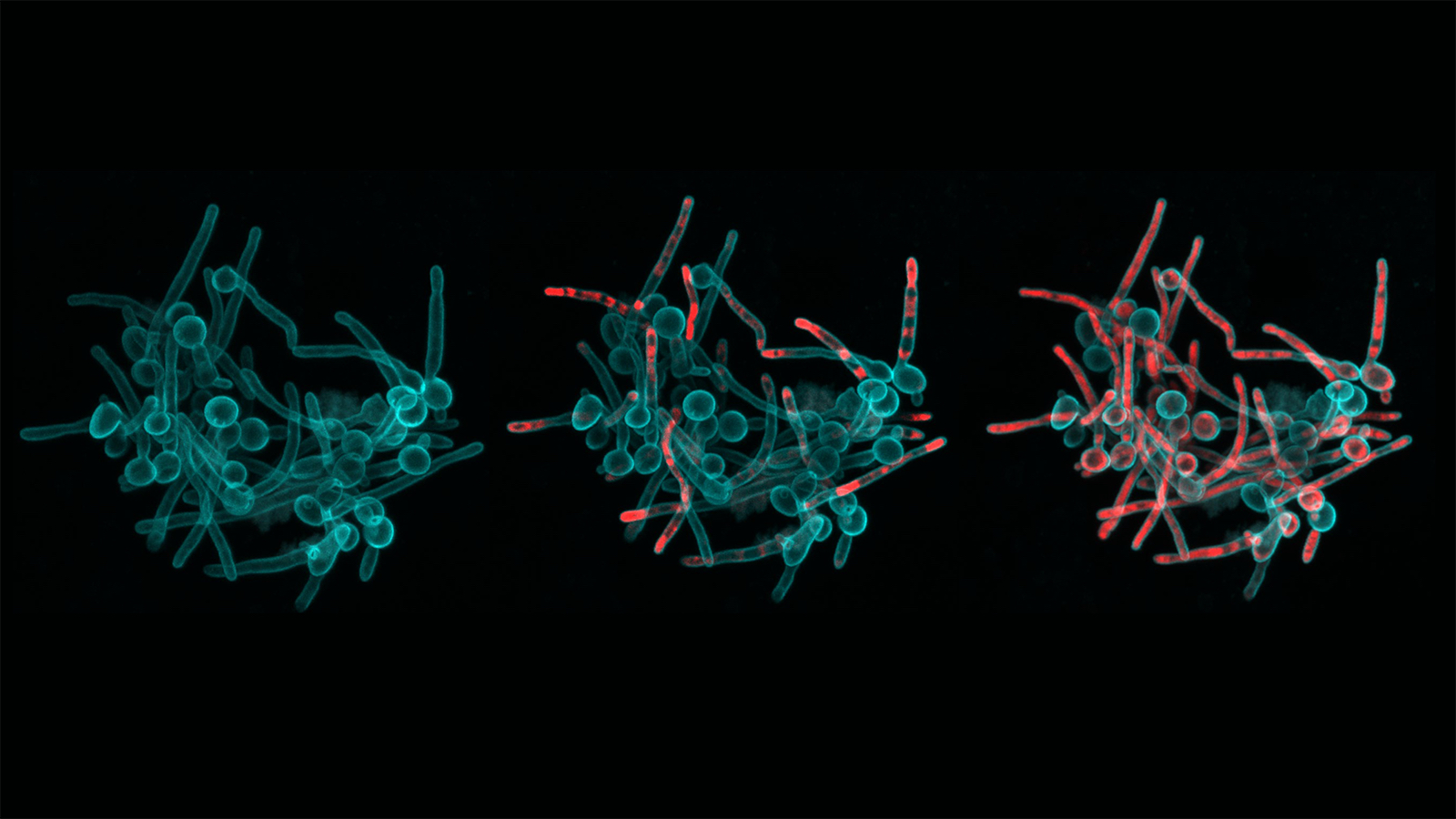
A task led by CiPD core member and Penn Dental Medication professor Henry Daniell won the Innovation in Dental Drugs and Engineering to Progress Oral Wellness (Notion) Prize, an award designed in partnership in between CiPD and the Penn Center for Wellbeing, Units, and Technology, or Penn Wellbeing Tech. That recognition will enable fund a project Daniell is pursuing with Daeyon Lee of Penn Engineering and some others to make a plant-dependent chewing gum that can degrade dental plaque and potentially even provide biopharmaceuticals to cut down infectious particles of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva.
An additional Centre-supported prize, the inaugural Advancing Oral and Craniofacial Health and fitness Award, less than the umbrella of Penn Wellness Tech Accelerator software, was lately bestowed on Eugene Ko of Penn Dental Medication. He and Shu Yang of Penn Engineering are producing a specialized bottle process to boost feeding and growth results for children born with cleft palates.
The Center’s operate is earning awareness from within the College and perfectly over and above. Koo was named Emerging Inventor of the Year at the Penn Centre for Innovation’s 2020 awards ceremony, recognizing his use of nanoparticles and microrobots to get rid of biofilms, this sort of as dental plaque.
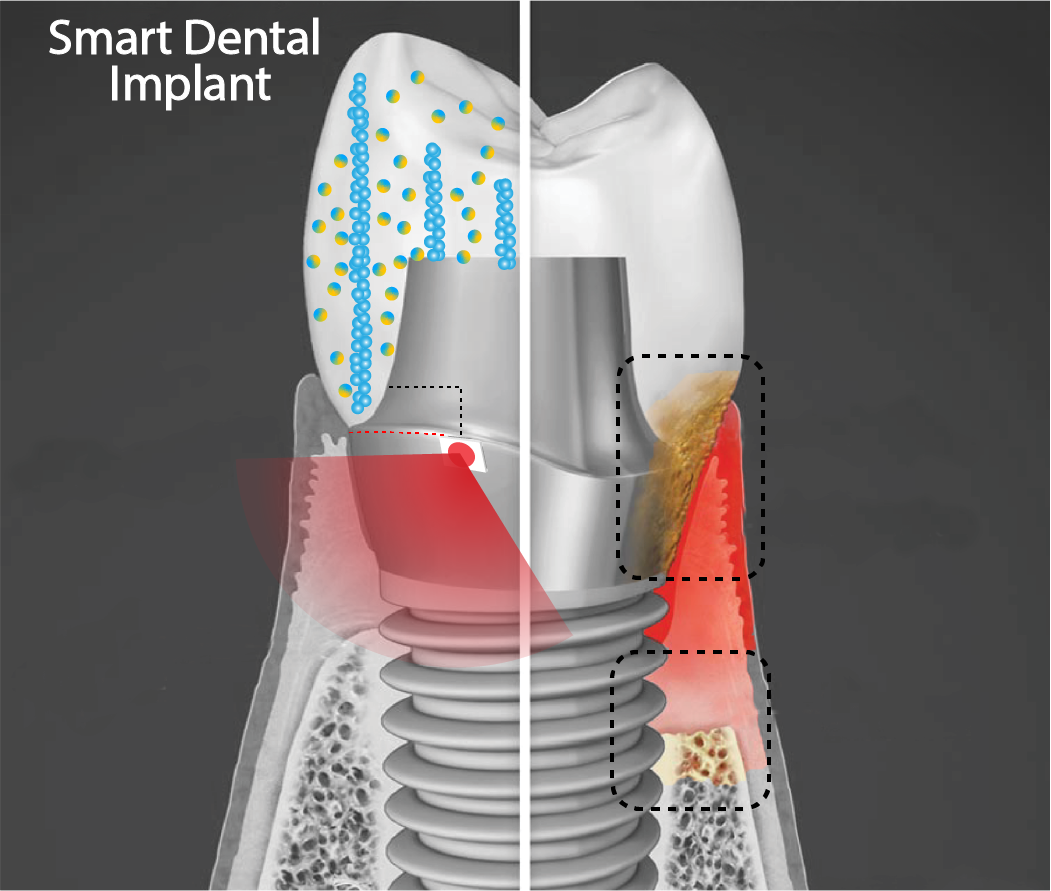
On a worldwide stage, the Worldwide Association for Dental Analysis introduced past 7 days that Penn’s César de la Fuente, a Presidential Assistant Professor with joint appointments in the Penn Medication and Penn Engineering, and Koo, his co-investigator, won the organization’s 2021 Innovation in Oral Wellness Treatment Award. Their venture, producing a reduced-value mouthguard that can sense biomarkers in saliva for the rapid detection of pathogens, will obtain $50,000 to continue on advancing the technological know-how towards scientific software.
When however in its early times, CiPD’s grand ambitions are currently transforming into development in labs close to campus. And partnerships with Penn Dental Medicine’s Centre for Clinical and Translational Study, Penn Health and fitness Tech, IBI, and the Penn Center for Innovation will speed that development into biotechnologies that, one particular working day soon, may perhaps have a tangible impact on care.
“There is a substantial possibility right here to revolutionize the industry of dental medication by integrating engineering,” says Koo. Adds Stebe: “And to prepare the professionals at the forefront of the two fields.”
Hyun (Michel) Koo is a professor in the Department of Orthodontics, Division of Local community Oral Overall health, and Division of Pediatric Dentistry in the College of Pennsylvania College of Dental Medication and co-director of the Heart for Innovation & Precision Dentistry.
Kathleen Stebe is the Richer & Elizabeth Goodwin Professor in the Section of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering in Penn’s School of Engineering and Utilized Science and co-director of the Middle for Innovation & Precision Dentistry.